In Growing Sustainability - Part 1 I lauded the War Commission Gardens and Victory Gardens for what they grew, a lot of food and a more self-sufficient citizenry. At their height, over 20,000,000 Victory Gardens dotted the American landscape and in 1944, they were producing 40% of all the vegetables grown in the US. These small scale but widespread gardens and orchards contributed to the food landscape in many subtle ways beyond just the food produced on them. A diversity of growers and a diversity of what is grown seems to go hand-in-hand.This startling illustration by the Rural Advancement Foundation International-USA depicts the realities of our dwindling agricultural biodiversity with a sampling of the commercially available varieties of 10 commonly grown vegetable seeds from seed houses in 1903 at the top of the chart and the dramatic reduction in varieties of those same vegetables at the National Center for Genetic Resources Preservation just 80 years later.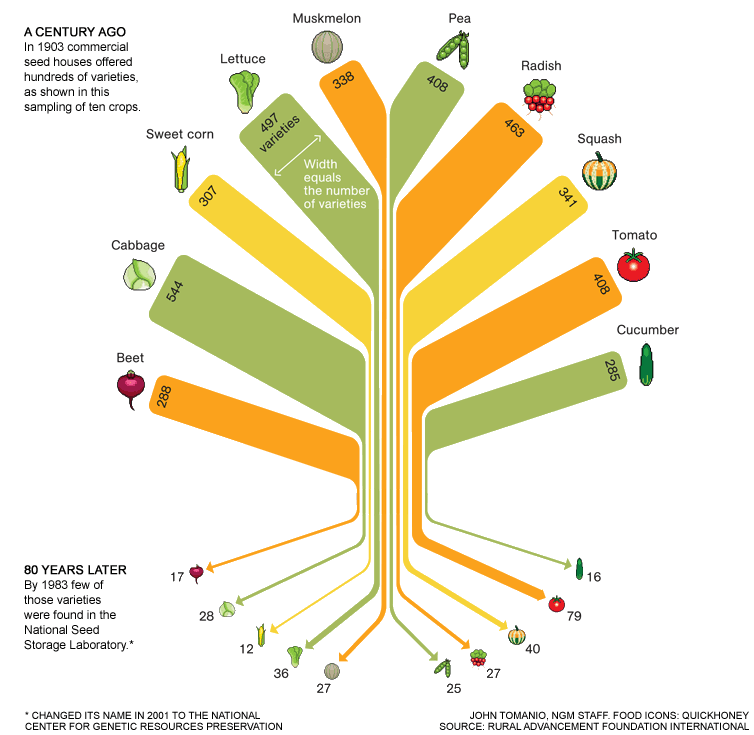 And it is not just the 1o varieties shown above that are at risk - this article by National Geographic puts the estimated diversity loss of all historic fruits and vegetables for the US at 90% while this Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations article puts the total global decrease of plant diversity at 75% in the last century.But there is good news in the What's For Dinner in 2025 discussion as well. Recessions spur backyard growing in a big way because growing your own food is cheaper than buying it. And this last recession happened in the age of the internet! How to plant, grow and harvest videos populate YouTube and sites like Garden Girl TV. Online seed houses for heirloom and open pollinated seeds have exploded in number and serve to connect the growers to a growing variety of available seeds. Two of my favorites are Baker Creek Heirloom Seeds and Seed Savers Exchange. Countless rural and urban farmers have blogs and vlogs, sharing their successes and failures and creating online communities that are (excuse the pun) growing.Whether the online/rural/suburban/urban agricultural movement of people growing food where ever they live will be able to sustain itself over the long haul is anyone's guess. So a further bit of good news for future agricultural diversity is that Cary Fowler, along with the Consultative Group on International Agricultural Research (CGIAR) created the Svalbard Global Seed Vault to serve as a salt mine style back up of seeds from gene banks all over the world.Every minute of Cary's charming, engaging, sometimes scary* and ultimately uplifting 2009 TED Talk is worth watching!* At the 8:30 mark he talks about the the extremely limited time (2 breeding cycles) that plant breeders have to get corn ready for the climate of 2030. In the context of today's GMO headlines, it is easy to forget that injecting genes into a food crop does not make "food". It makes a plant organism that still has to grow to sexual maturity, be crossed with another plant to even get the first round of seed to test.
And it is not just the 1o varieties shown above that are at risk - this article by National Geographic puts the estimated diversity loss of all historic fruits and vegetables for the US at 90% while this Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations article puts the total global decrease of plant diversity at 75% in the last century.But there is good news in the What's For Dinner in 2025 discussion as well. Recessions spur backyard growing in a big way because growing your own food is cheaper than buying it. And this last recession happened in the age of the internet! How to plant, grow and harvest videos populate YouTube and sites like Garden Girl TV. Online seed houses for heirloom and open pollinated seeds have exploded in number and serve to connect the growers to a growing variety of available seeds. Two of my favorites are Baker Creek Heirloom Seeds and Seed Savers Exchange. Countless rural and urban farmers have blogs and vlogs, sharing their successes and failures and creating online communities that are (excuse the pun) growing.Whether the online/rural/suburban/urban agricultural movement of people growing food where ever they live will be able to sustain itself over the long haul is anyone's guess. So a further bit of good news for future agricultural diversity is that Cary Fowler, along with the Consultative Group on International Agricultural Research (CGIAR) created the Svalbard Global Seed Vault to serve as a salt mine style back up of seeds from gene banks all over the world.Every minute of Cary's charming, engaging, sometimes scary* and ultimately uplifting 2009 TED Talk is worth watching!* At the 8:30 mark he talks about the the extremely limited time (2 breeding cycles) that plant breeders have to get corn ready for the climate of 2030. In the context of today's GMO headlines, it is easy to forget that injecting genes into a food crop does not make "food". It makes a plant organism that still has to grow to sexual maturity, be crossed with another plant to even get the first round of seed to test.
Growing Sustainability - Part 1
 I have three 24 x 36 cork boards in my home office, devoted to helping me organize my garden. They are filled with seasonal planting guides for Zone 7, my own garden plans for seasonal and succession plantings, companion planting charts and the listings of vegetables by family that make sense of them.Interspersed between these work-a-day printouts are some of my favorite images of the WWI National War Garden Commission (1910-1920) and WWII Victory Garden (1930-1950) posters. I have long been a fan of these nostalgic images for what they represented at the time and what they represent to me* today.The images, although quaint and nostalgic now, when they were produced were part of a bold initiative that is difficult to imagine ever repeating itself in the light of 21st century politics. The world leaders at that time asked of their people to be a little more self-sufficient for a while, to do a little more for themselves and consume less, not for any immediate personal benefit for those making the sacrifices of growing and preserving their own food, but for "the greater good". They also represent a generally accepted, society endorsed back to the land movement long before the Foxfire books of the 1970s solidified in the public mind that unless you are a farmer by trade, growing a significant portion of your own food is a hallmark of an alternative lifestyle.With the War Gardens of WWI and later the Victory Gardens of WWII, ordinary households economized during rationing. They grew, ate, canned and preserved some of their own produce to nourish their families and to help the war efforts by using less of the nation's production and transportation resources so those resources would be available elsewhere.It was a time of lofty and aspirational ideals and pulling together for a purpose larger than ourselves. Some of the growing ideas and solutions promulgated during that period, particularly of WWII were a mix of good and pretty bad, but the overall concept was a good one - a decentralized food system, self-sufficient citizens and a government system that supported the bootstraps mentality that has become a hallmark of those generations.
I have three 24 x 36 cork boards in my home office, devoted to helping me organize my garden. They are filled with seasonal planting guides for Zone 7, my own garden plans for seasonal and succession plantings, companion planting charts and the listings of vegetables by family that make sense of them.Interspersed between these work-a-day printouts are some of my favorite images of the WWI National War Garden Commission (1910-1920) and WWII Victory Garden (1930-1950) posters. I have long been a fan of these nostalgic images for what they represented at the time and what they represent to me* today.The images, although quaint and nostalgic now, when they were produced were part of a bold initiative that is difficult to imagine ever repeating itself in the light of 21st century politics. The world leaders at that time asked of their people to be a little more self-sufficient for a while, to do a little more for themselves and consume less, not for any immediate personal benefit for those making the sacrifices of growing and preserving their own food, but for "the greater good". They also represent a generally accepted, society endorsed back to the land movement long before the Foxfire books of the 1970s solidified in the public mind that unless you are a farmer by trade, growing a significant portion of your own food is a hallmark of an alternative lifestyle.With the War Gardens of WWI and later the Victory Gardens of WWII, ordinary households economized during rationing. They grew, ate, canned and preserved some of their own produce to nourish their families and to help the war efforts by using less of the nation's production and transportation resources so those resources would be available elsewhere.It was a time of lofty and aspirational ideals and pulling together for a purpose larger than ourselves. Some of the growing ideas and solutions promulgated during that period, particularly of WWII were a mix of good and pretty bad, but the overall concept was a good one - a decentralized food system, self-sufficient citizens and a government system that supported the bootstraps mentality that has become a hallmark of those generations. *Results may vary
*Results may vary